Edge Case Testing
Learn how to use Rock Smith's fuzzing variant generation to automatically create test flows that cover boundary conditions, invalid inputs, and security scenarios.
What Is Edge Case Testing
Edge case testing (also called fuzzing) automatically generates variations of your test flows to test scenarios that are often missed in manual testing. Starting from an existing flow, Rock Smith creates new child flows that test:
- Boundary values and limits
- Invalid and malformed inputs
- Special characters and encoding issues
- Security vulnerabilities
- Error handling and recovery
- Data format and localization edge cases
This helps you discover bugs and vulnerabilities without manually creating dozens of test variations.
Scenario Types
Rock Smith generates edge cases across 15 scenario categories organized into three groups:
Core Scenarios
| Scenario Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Boundary Values | Min/max values, empty strings | Max length, zero, negative numbers |
| Invalid Format | Malformed emails, dates, phone numbers | Invalid email, wrong date format |
| Special Characters | SQL injection, XSS, Unicode | Unicode, emojis, control characters |
| Field Length | Too long/short strings | Empty, very long, exact max length |
| Type Mismatch | Wrong data types | Text in number field, numbers in text |
| Required Field | Missing required fields | Empty required fields, null values |
| State Transition | Invalid workflow states | Skip steps, repeat actions, back navigation |
Security Scenarios
| Scenario Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication Bypass | Test auth vulnerabilities | Direct URL access, session manipulation |
| Authorization Escalation | Test permission boundaries | Access other user's data, admin functions |
| Injection Attack | SQL and command injection | SQL in inputs, shell commands |
| XSS Variants | Cross-site scripting tests | Script tags, event handlers, encoded payloads |
Data Scenarios
| Scenario Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Encoding Issues | Character encoding problems | UTF-8/ASCII mismatches, special encoding |
| Localization | Locale-specific testing | Date formats, number separators, currencies |
| Null Handling | Null/undefined values | Null in required fields, undefined properties |
| Whitespace | Whitespace variations | Leading/trailing spaces, tabs, newlines |
Generating Fuzzing Variants
From an Existing Flow
Generate fuzzing variants from any saved flow:
- Open a flow from your Flows list
- Click the Generate Fuzzing Variants button (beaker icon)
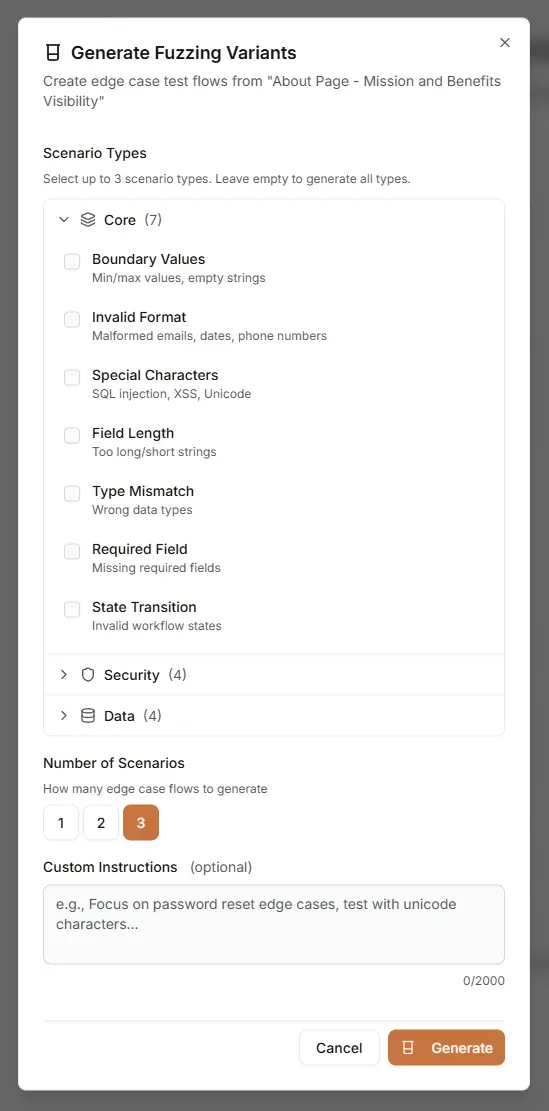
- Configure generation options in the dialog:
- Scenario Types: Select up to 3 types from Core, Security, or Data categories
- Number of Scenarios: Choose 1, 2, or 3 variants to generate
- Custom Instructions: Add optional guidance for the AI (max 2000 characters)
- Click Generate
- Review generated variants in the flow tree
Configuration Options
Scenario Type Selection
Choose which scenario types to include from three collapsible categories:
- Core: 7 types for functional edge case testing (boundary values, formats, field validation)
- Security: 4 types for penetration and security testing (injection, XSS, auth bypass)
- Data: 4 types for data handling edge cases (encoding, localization, null handling)
Select up to 3 scenario types, or leave empty to generate variants across all types.
Number of Scenarios
Control how many variants are generated per request:
- 1: Quick single variant generation
- 2: Moderate coverage with two variants
- 3: Maximum variants per generation request
Custom Instructions
Provide specific guidance to focus the AI on particular edge cases:
- Target specific input fields or form elements
- Focus on particular vulnerability types
- Test specific business logic scenarios
- Example: "Focus on password reset edge cases, test with unicode characters"
Understanding the Flow Tree
Fuzzing variants are organized in a hierarchical tree structure with a maximum depth of 6 levels:
Login Flow (depth 0, baseline)
├── Empty Email (depth 1, boundary_value)
│ └── Whitespace-only Email (depth 2, whitespace)
│ └── Unicode Email (depth 3, encoding_issues)
├── SQL Injection in Email (depth 1, injection_attack)
│ └── Encoded SQL Injection (depth 2, special_characters)
├── XSS in Email (depth 1, xss_variants)
└── Empty Password (depth 1, required_field)
└── Whitespace-only Password (depth 2, whitespace)
Flow Tree Navigation
Use the Flow Map navigator (map icon in the toolbar) to quickly browse and navigate your flow tree structure:
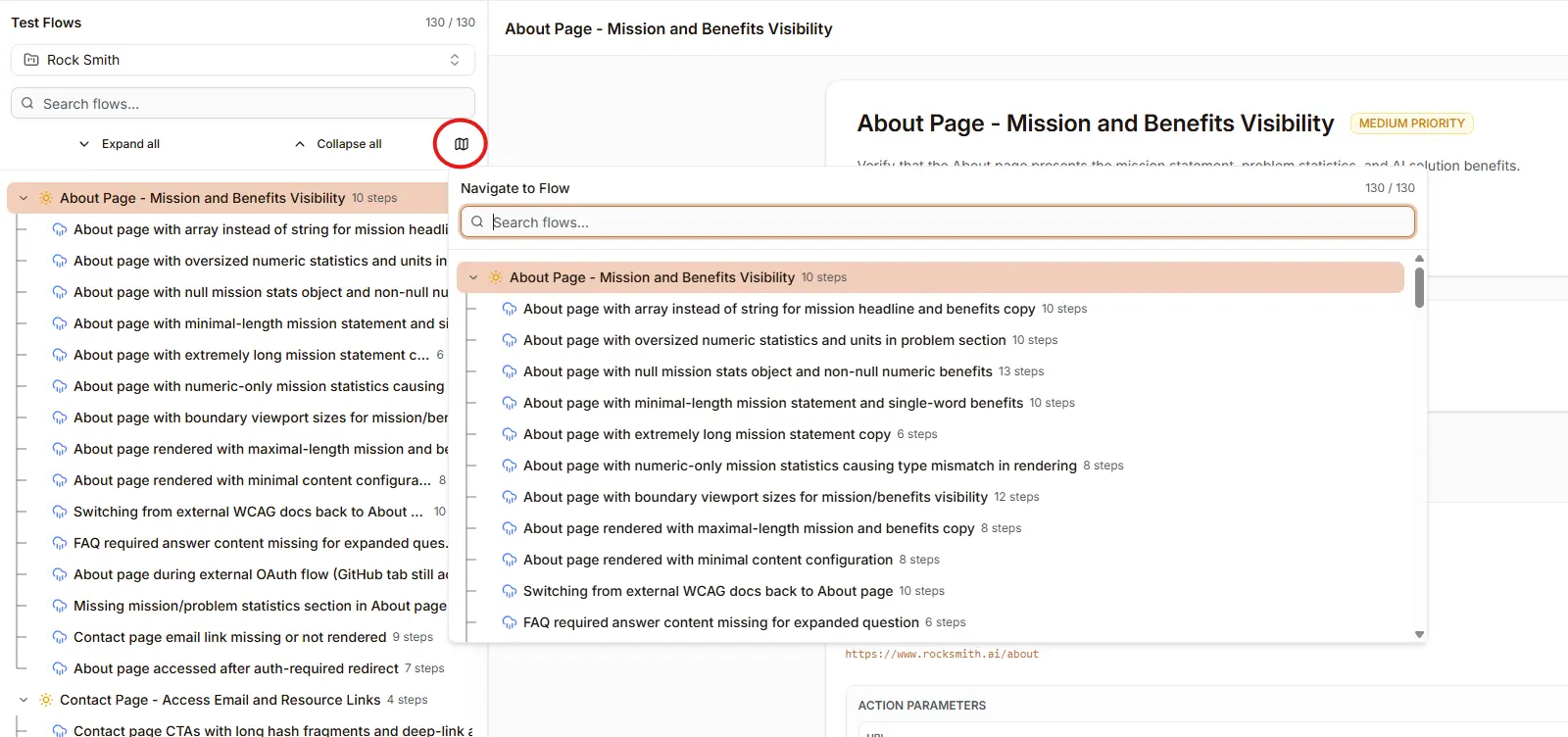
The flow map provides:
- Search: Filter flows by name
- Tree View: Collapsible hierarchy showing all flows and variants
- Step Counts: See how many steps each flow contains
- Quick Navigation: Click any flow to select it
Tree Concepts
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Baseline Flow | The original flow (depth 0) |
| Parent Flow | The flow a variant was generated from |
| Root Flow | The original baseline at the top of the tree |
| Depth | Level in the tree (0 = baseline, max = 6) |
Nested Generation
You can generate fuzzing variants from existing variants to explore deeper edge cases:
- Run the baseline flow
- Generate first-level fuzzing variants
- Select an interesting variant
- Generate additional variants from it
- Build deeper test coverage (up to depth 6)
This allows you to explore complex scenarios like "SQL injection with special character encoding" or "authentication bypass with localized input."
Note: Fuzzing generation is restricted at depth 6 to prevent excessively deep trees.
Running Edge Case Tests
Execute Individual Variants
Run a single fuzzing variant:
- Select the variant in the flow tree
- Click Run Flow
- Configure execution options
- Review results
Batch Execution
Run multiple variants together:
- Select the parent flow
- Click Run with Variants
- Choose which variants to include
- Start batch execution
- Review aggregated results
Analyzing Results
Edge case results show:
- Pass/Fail Status: Did the application handle the edge case correctly?
- Error Behavior: How did the app respond to invalid input?
- Security Findings: Were vulnerabilities detected?
- Screenshots: Visual state during edge case execution
Security Testing
Using Security Scenarios
Security scenario types are designed to find vulnerabilities:
Injection Testing
The Injection Attack scenario generates:
- SQL injection payloads
- NoSQL injection patterns
- Command injection attempts
- LDAP injection tests
XSS Testing
The XSS Variants scenario generates:
- Script tag injections
- Event handler payloads
- Encoded XSS patterns
- DOM-based XSS attempts
Authentication Testing
The Authentication Bypass scenario tests:
- Direct URL access without login
- Session fixation vulnerabilities
- Cookie manipulation
- Token bypass attempts
Authorization Testing
The Authorization Escalation scenario tests:
- Horizontal privilege escalation (accessing other users' data)
- Vertical privilege escalation (accessing admin functions)
- IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference) vulnerabilities
Security Best Practices
- Test in staging: Run security fuzzing variants in non-production environments
- Review findings carefully: Not all failures indicate vulnerabilities
- Prioritize critical flows: Focus security testing on authentication, payments, data access
- Regular testing: Run security fuzzing variants after each major change
Best Practices
Flow Design for Fuzzing
- Use clear input steps: Well-defined inputs generate better edge cases
- Add meaningful assertions: Assertions help detect edge case failures
- Include error handling steps: Test that errors are handled gracefully
Variant Management
- Name variants clearly: Use descriptive names for easy identification
- Delete unused variants: Keep your flow tree clean
- Document findings: Note which edge cases revealed issues
- Monitor tree depth: Keep depth reasonable (recommended: 3-4 levels for most use cases)
Testing Strategy
- Start with core types: Test boundary values and formats first
- Add security types for critical flows: Focus security testing where it matters
- Use data types for internationalization: Test encoding and localization for global apps
- Iterate based on findings: Generate more variants in problem areas
- Balance coverage and cost: Not every flow needs every scenario type
Troubleshooting
Fuzzing Variants Not Generating
- Check flow has inputs: Edge cases require input fields to modify
- Verify flow is saved: Unsaved flows cannot generate variants
- Review step definitions: Unclear steps may not fuzz well
- Check depth limit: Generation is disabled at depth 6
Unexpected Failures
- False positives: Some edge cases may fail due to expected validation
- Timing issues: Add wait steps if edge cases fail due to slow responses
- Session problems: Use browser profiles for authenticated edge case testing
Too Many Variants
- Limit scenario types: Select only relevant categories (max 3 types)
- Reduce variant count: Start with 1 variant per request
- Focus on specific steps: Target high-risk inputs only
Next Steps
- Working with Flows - Create flows to generate fuzzing variants from
- Personas - Test with different user behaviors
- Managing Credits - Optimize edge case testing costs
- Discovery Sessions - Find flows to test with edge cases